How to implement decentralized exchange in ink! smart contract language
Author's intention while building the tutorial
The Rust programming language is not obvious, and delivering ink! smart contracts is not an easy task, especially for newbies. In this space, there are very few fully working examples. My main goal while writing the tutorial was to provide simple, yet fully functioning source code that is ready to run, along with unit tests that are also ready to run.
I encourage you to explore the whole source code of the decentralized exchange code and unleash your creativity to enhance it. There is no better approach to learning than by actively engaging with the code, conducting experiments, and making improvements in a live environment.
If you are interested in more learning and development of the smart contract one of the option is to implement proxy pattern. That is an example of improvement proposal that actually adds real value.
How to Build Decentralized Exchange in ink! Smart Contract Programming Language
A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a type of cryptocurrency exchange that operates on a blockchain network without the need for intermediaries or a central authority. It allows users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other using smart contracts. DEXs provide increased security and privacy as they eliminate the need to trust a centralized entity with users' funds. They also offer a more transparent and censorship-resistant trading environment, empowering users to have full control over their assets.
ink! is a programming language specifically designed for developing smart contracts on the Polkadot blockchain ecosystem. It is a statically-typed language that emphasizes safety, correctness, and efficiency.
What you will build
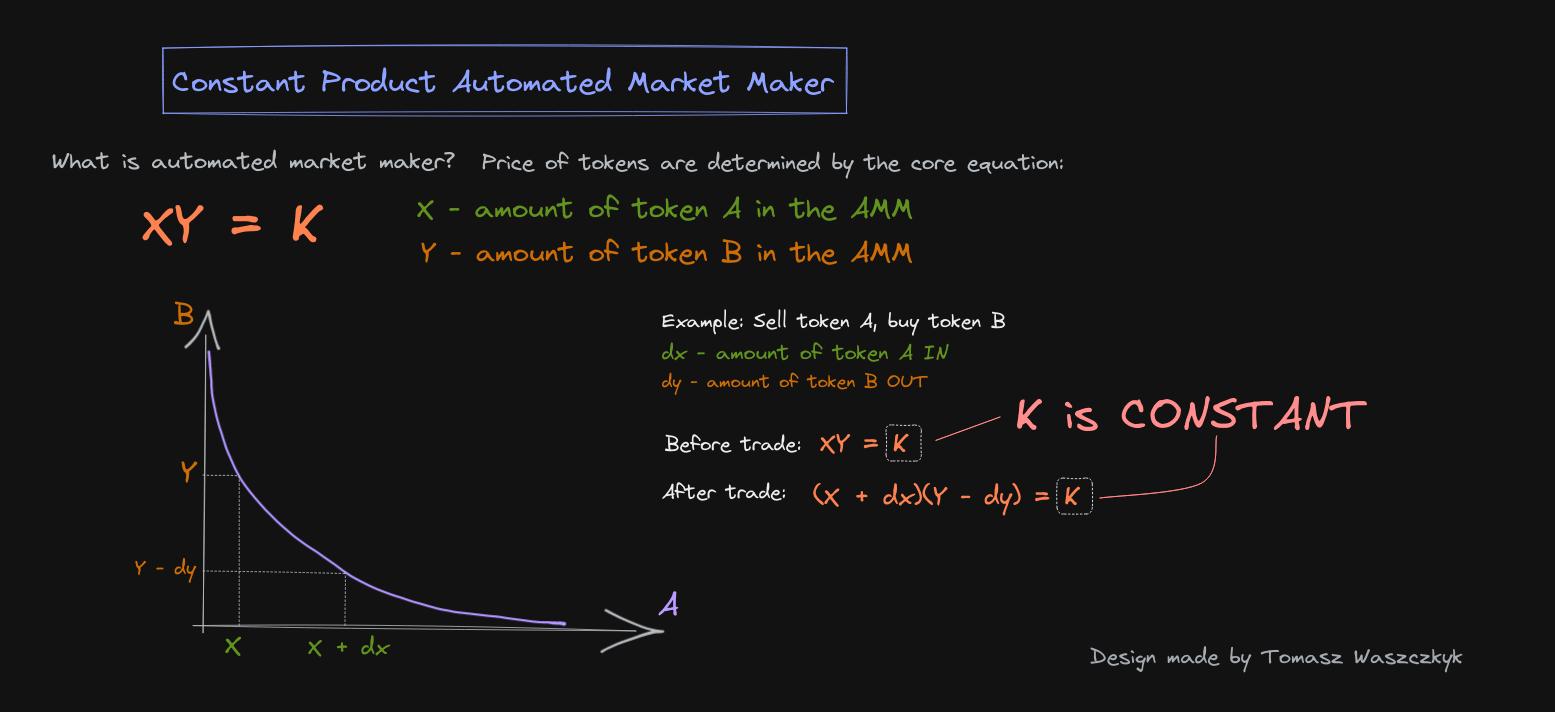
An Automated Market Maker (AMM) is a decentralized exchange model that relies on a mathematical price formula to facilitate asset trading. Instead of using a traditional order book and relying on buyers and sellers, AMMs utilize liquidity pools where assets are priced based on a specific algorithm.
Uniswap, for instance, employs the formula p * q = k, where p represents one token's amount in the pool, and q represents the amount of the other token.
The constant k ensures that the total liquidity remains unchanged. As an example, when a volatile asset like A is purchased, its price increases due to reduced availability in the pool, while the price of asset B decreases as its availability increases.
The pool maintains balance, with the total value of A always equaling the total value of B, and expands only when new liquidity providers participate.
Time of completion
- 4-8 hours
What you'll learn
I do believe that learning by doing and making experiments is the best way to gain more experience that is especially important for delivering smart contracts. The tutorial shows you:
- how works basic decentralized exchange
- how to implement ink! smart contract
- unit testing of the smart contract
- how to handle errors in the smart contracts written in ink! language
Prerequisites
- basic knowledge of Rust programming language
cargobuild tool- preferred Linux-like operating system (optional)
- willingness for learning and curiosity
Author
- Tomasz Waszczyk is a software engineer that is perpetually curious, despite the pain accompanying such curiosity.